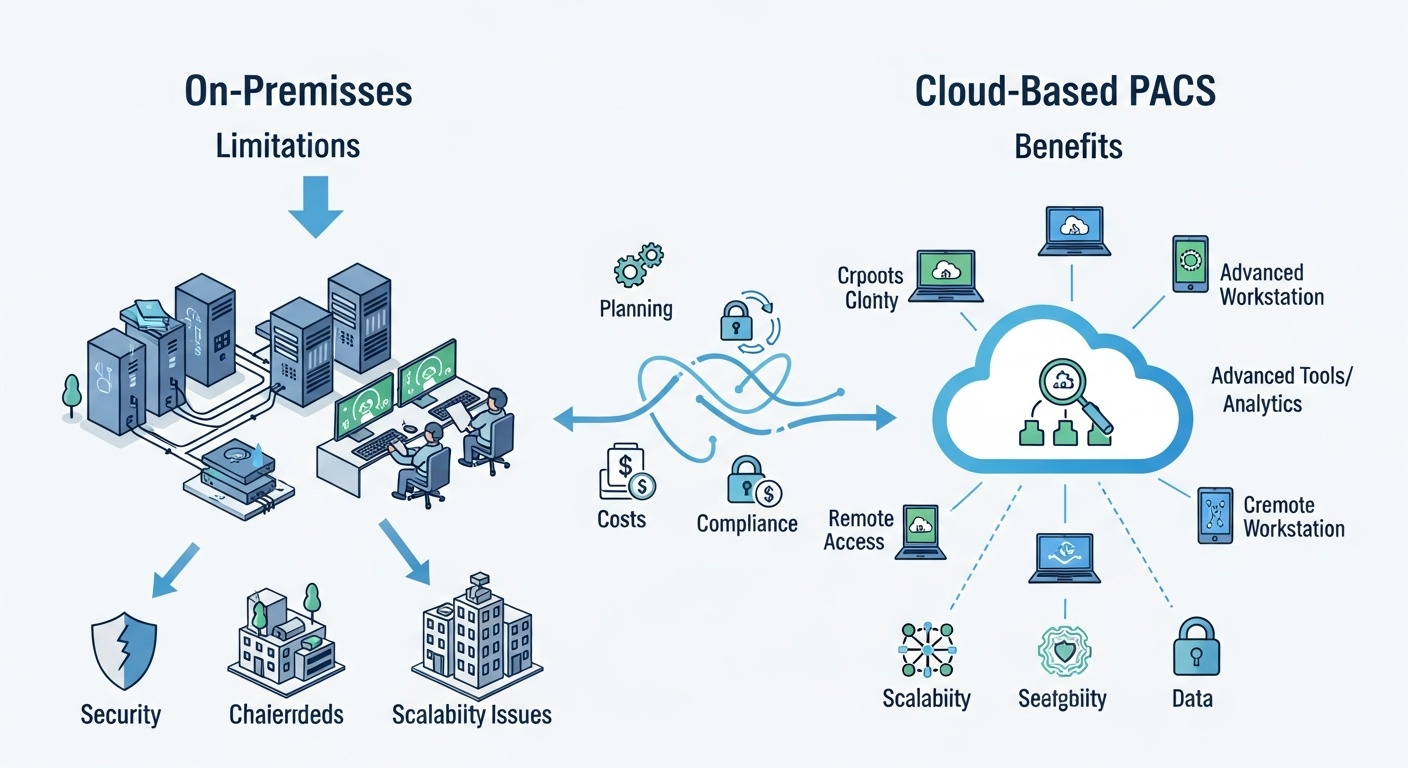
Migrating a hospital or clinic’s on-premises PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) to a cloud-based solution is a transformative step. It promises improved accessibility, scalability, and operational efficiency, but the path to the cloud is complex.
Imaging data is critical not just for daily clinical operations, but it is also highly regulated, requiring compliance with standards like HIPAA or GDPR. A poorly planned migration can disrupt workflows, compromise data integrity, and introduce unexpected costs.
Yet, when executed thoughtfully, moving to a cloud PACS opens doors to advanced tools, remote accessibility, and future-ready infrastructure.
Traditional on-premises PACS relies heavily on physical servers, storage arrays, and IT teams for maintenance. Hardware requires frequent upgrades, consumes significant power, and demands ongoing monitoring. Storage limitations can become bottlenecks as imaging datasets grow, and expanding capacity often involves costly investments. Remote access is cumbersome, hindering telemedicine and multi-site collaboration. Disaster recovery and redundancy require additional infrastructure and planning, often stretching hospital budgets and staff resources.
Cloud PACS offers an alternative: elasticity, centralized updates, secure access from anywhere, and automated disaster recovery. Hospitals can scale storage and compute dynamically, accommodate growing modality outputs, and provide clinicians with immediate access to images without being tethered to local servers. The cloud also enables integration with AI tools, analytics platforms, and collaborative applications that on-premises systems struggle to support.
Before embarking on migration, a thorough assessment of the current PACS environment is essential. Hospitals should inventory all imaging modalities (e.g., CT, MRI, X-ray, ultrasound, PET, and nuclear medicine) and document storage size, data growth rates, and the age of datasets. Equally important is understanding workflows: which images are critical for daily operations, which systems are integrated with PACS (RIS, EHR, billing), and how data moves across departments.
Metadata consistency is another crucial consideration. Patient identifiers, accession numbers, and study descriptions must be accurate and standardized to prevent errors after migration. Hospitals should also review compliance requirements, retention policies, and data residency regulations, as these factors will influence vendor selection and migration methods.
Selecting a cloud PACS provider is one of the most critical steps in the migration journey. Not all “cloud” solutions are truly cloud-native; some are merely virtualized versions of legacy PACS, which may limit scalability and flexibility. Key criteria include:
• True Cloud-native Architecture For Elastic Storage And Compute.
• Full Support For Dicom Protocols And Vendor-neutral Archives To Avoid Lock-in.
• Seamless Integration With Existing Ris, Ehr, And Reporting Systems Via Hl7 Or Fhir Standards.
• Strong Security Features, Including Encryption At Rest And In Transit, Access Controls, And Audit Logs.
• Regional Data Center Options To Reduce Latency And Comply With Data Residency Laws.
• Transparent Pricing, Predictable Support Services, And A Proven Migration Roadmap.
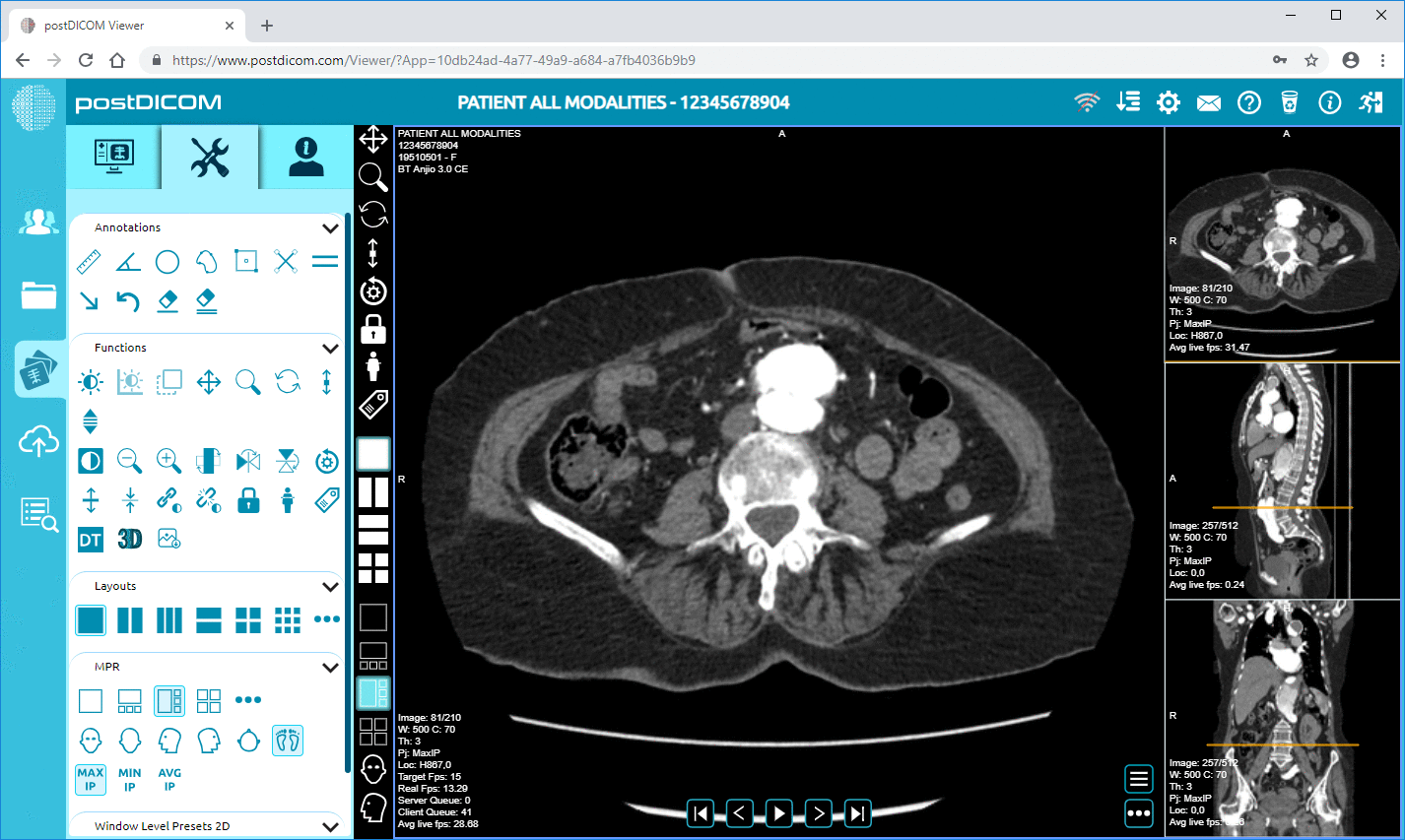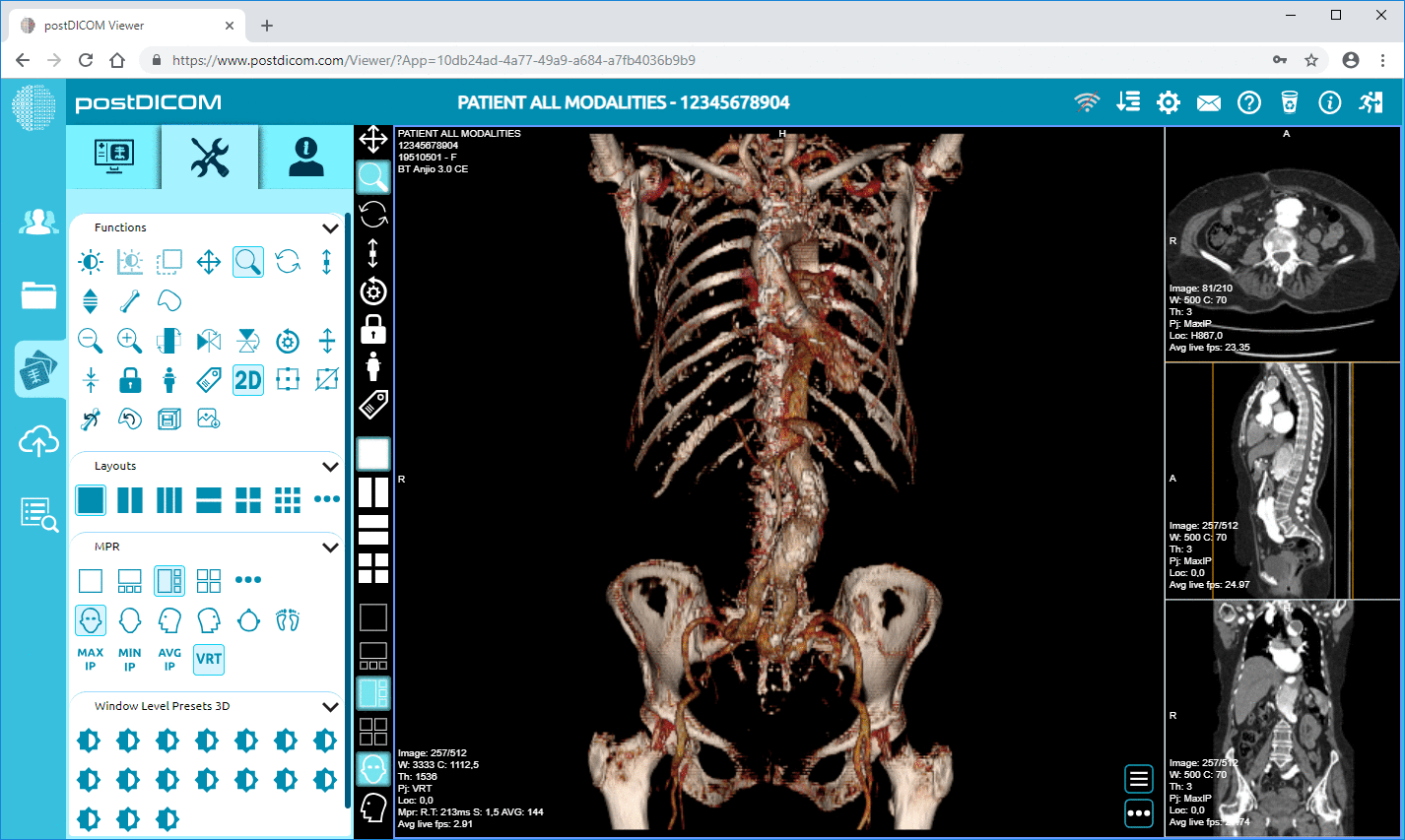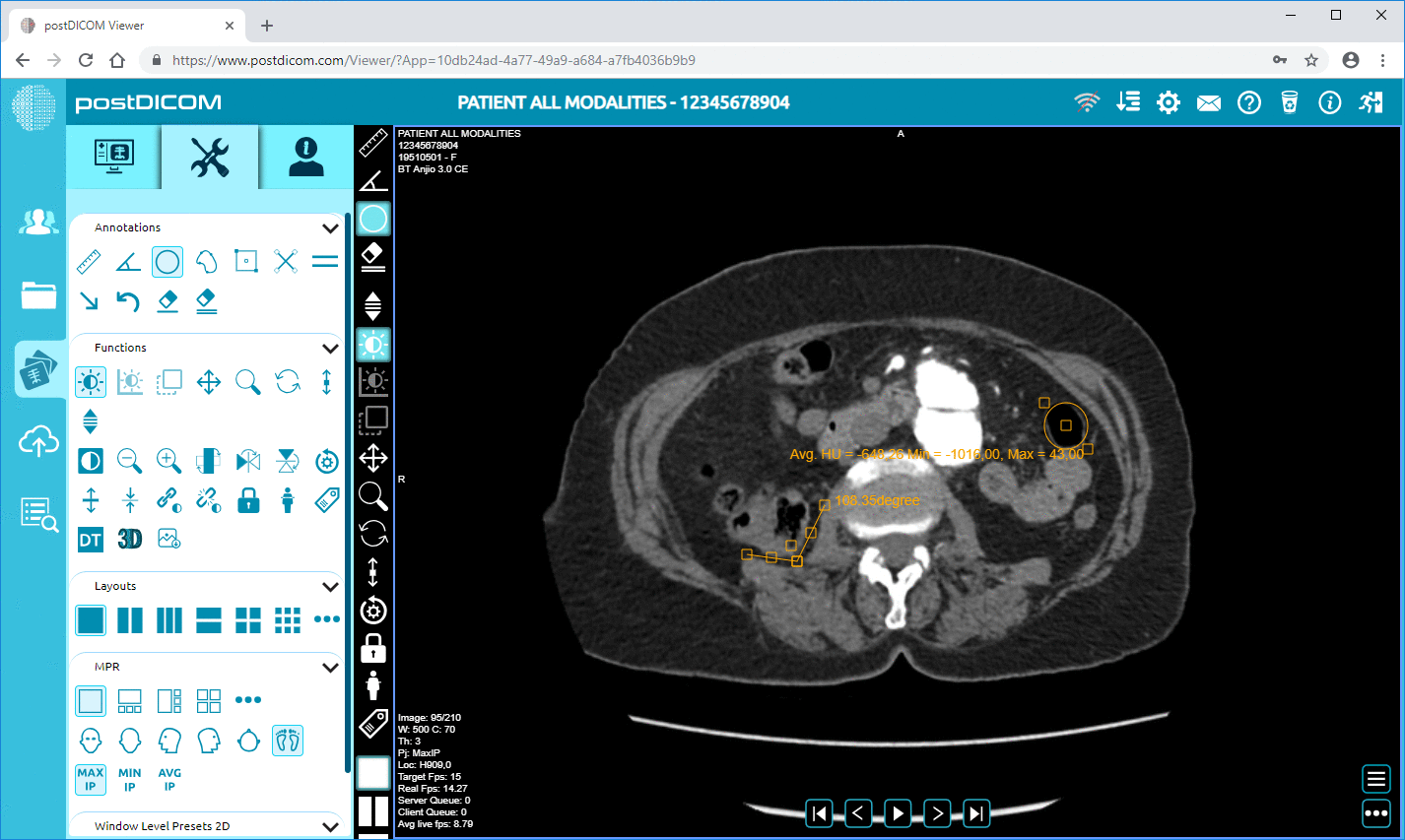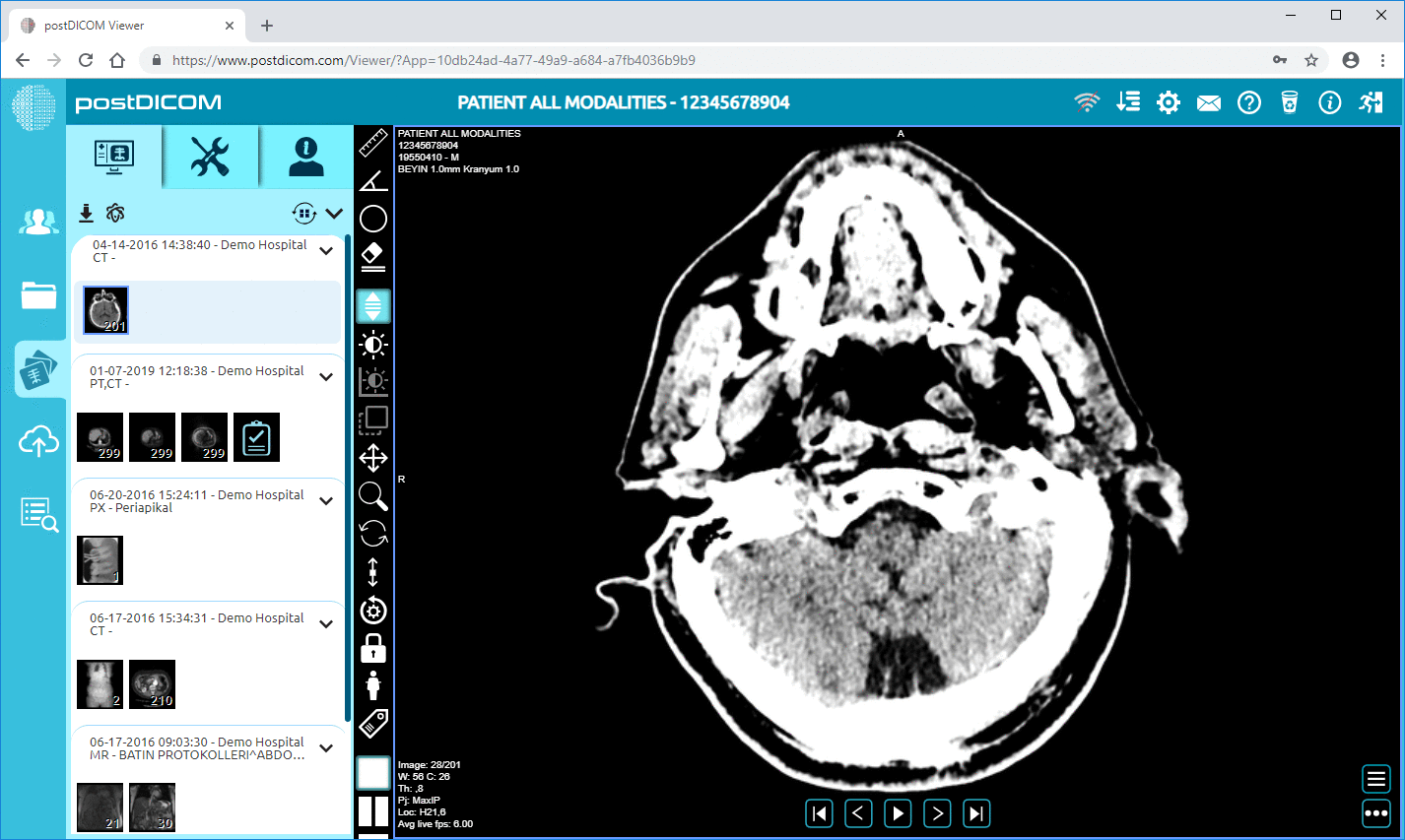
PostDICOM exemplifies a cloud PACS solution built to address these needs. It offers secure, scalable storage, zero-footprint diagnostic viewers, and robust integration capabilities. Hospitals can test PostDICOM with a free trial to evaluate workflows, import sample data, and verify performance before fully committing.
A well-defined migration strategy minimizes operational disruption and mitigates risk. Hospitals typically choose between three approaches:
• Big Bang Migration: All data is moved at once. This approach can be faster but carries higher risk, as any errors affect the entire archive.
• Phased Migration: Data is moved incrementally—by modality, patient population, or time frame—allowing IT teams to validate each phase and resolve issues before proceeding.
• Hybrid Approach: Recent studies are migrated first to the cloud while older archives remain on-premises until synchronization is complete.
The choice depends on operational tolerance for downtime, data volume, network bandwidth, and resource availability. Regardless of approach, planning should include fallback strategies, clear timelines, and defined responsibilities across IT, radiology, and clinical teams.
Data preparation is often underestimated, yet it is critical to success. This stage involves cleaning and standardizing DICOM headers, reconciling metadata, and removing duplicates. Consistency in patient identifiers and accession numbers is crucial for maintaining integrity during transfer. Some datasets may require conversion to standard DICOM format or transformation to match the cloud PACS schema. Accurate metadata mapping ensures images are searchable and retrievable after migration, avoiding disruptions in clinical workflows.
 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
The transfer itself is both a technical and logistical challenge. Imaging datasets can easily exceed hundreds of terabytes. Hospitals must carefully plan network utilization to avoid bandwidth bottlenecks, often opting for bulk data transfers via dedicated high-speed connections or physically shipped storage devices for initial seeding. Incremental streaming is used to synchronize new studies during migration. Throughout this process, validation mechanisms such as checksums and hash verification confirm data integrity.
Integration with existing systems is another critical task. Modalities like CT, MRI, and ultrasound must be redirected to the cloud PACS, while RIS and EHR systems continue to operate seamlessly. Post-migration testing involves validating image retrieval times, checking metadata integrity, and ensuring reporting workflows function without disruption. Keeping the on-premises PACS operational as a fallback during migration helps safeguard against unexpected issues.
After the migration, hospitals can optimize workflows to maximize cloud capabilities. Tiered storage allows frequently accessed studies to reside on high-speed storage while older studies move to cost-effective cold storage. Automated archiving and retention policies maintain compliance and efficiency. Cloud PACS platforms also support integration with AI and analytics tools, enabling advanced diagnostics and population-level insights. Continuous monitoring of system performance and user feedback ensures operational standards are maintained.
Challenges are inevitable. Security concerns demand robust encryption, access controls, and auditing. Latency issues can affect radiologists’ ability to view large studies remotely, which may require caching strategies or regional data center selection. Vendor lock-in is a risk if proprietary formats or restrictive export options are used, making standard DICOM and VNA support essential. Hospitals must also account for hidden costs such as data egress fees or unexpected storage overages. Finally, training and change management are vital to ensure clinical and IT staff adopt new workflows efficiently.
PostDICOM addresses these challenges with a cloud-native architecture designed for healthcare imaging. Its platform supports all standard DICOM modalities and vendor-neutral storage, while providing secure access, zero-footprint diagnostic viewers, and seamless integration with RIS and EHR systems.
Regional data center options reduce latency, and advanced security measures ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. PostDICOM’s 7 Days free trial allows hospitals to test real-world workflows, evaluate performance, and familiarize staff with the cloud environment before a full-scale migration, reducing risk and building confidence.
Migrating from on-premises PACS to cloud PACS is a complex, multi-faceted process that requires careful assessment, planning, execution, and optimization. Hospitals must evaluate their existing infrastructure, choose the right vendor, prepare and clean data, execute the transfer with validation, and optimize post-migration workflows.
Challenges such as security, latency, and vendor lock-in must be proactively addressed. When executed correctly, cloud PACS offers unmatched scalability, remote accessibility, disaster recovery, and advanced analytics capabilities that can transform clinical operations. PostDICOM provides a secure, flexible, and user-friendly solution to simplify this transition, with a free trial that allows organizations to experience the benefits firsthand before committing.
By approaching the migration strategically, hospitals can minimize disruption, maintain clinical excellence, and fully leverage the advantages of cloud technology to support patient care today and in the future.
|
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |