Teleradiology and telemedicine have revolutionized healthcare by enabling remote access to medical services, consultations, and diagnostics.
Central to these advancements is the crucial role played by medical imaging. One key technology that has significantly contributed to this progress is Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM).
In this blog, we will explore the importance of DICOM medical viewers in teleradiology and telemedicine, highlighting their functionality, features, and impact on healthcare delivery. We will delve into the components and advantages of DICOM, discuss popular viewer software options, and examine the challenges and considerations surrounding their use.
As we navigate this fascinating topic, we'll discover how DICOM medical viewers continue to shape the future of medical imaging and its integration into modern healthcare.
DICOM medical viewers have been instrumental in enabling teleradiology by providing radiologists remote access to medical images.
Using these viewers, healthcare professionals can securely access and review images from various imaging modalities, such as X-ray, CT, MRI, and ultrasound, from any location with an internet connection.
This ability to review images remotely has expanded the reach of radiology services and improved healthcare delivery.
DICOM viewers facilitate better collaboration among radiologists, as they can easily share and discuss medical images with colleagues, regardless of their location. This enhanced communication leads to more accurate diagnoses, as multiple experts can weigh in on complex cases.
Additionally, teaching and learning opportunities for radiologists are amplified, as they can exchange insights and expertise across geographic boundaries.
Using DICOM medical viewers in teleradiology has significantly improved efficiency and reduced turnaround time for image interpretation.
By streamlining the workflow and enabling radiologists to access images remotely, these viewers help to expedite the diagnostic process. This increased efficiency is particularly beneficial in emergencies, where quick access to radiology reports can be critical for patient care.
DICOM viewers empower radiologists to provide real-time consultations and second opinions to their peers and referring physicians. These viewers facilitate quick and informed decision-making in patient care by allowing immediate access to medical images.
In challenging cases, seeking input from multiple experts can be invaluable in reaching an accurate diagnosis and selecting the most appropriate treatment plan. This collaborative approach helps to ensure the best possible patient outcomes.
DICOM medical viewers play a critical role in telemedicine by facilitating the seamless integration of medical images with Electronic Health Records (EHRs). This integration allows healthcare providers to access a patient's complete medical history, including diagnostic images, from a single platform.
As a result, physicians can make more informed decisions about patient care, leading to better outcomes and enhanced patient satisfaction.
Telemedicine relies on the ability to monitor and diagnose patients remotely. DICOM medical viewers enable physicians to access and review medical images from any location, providing essential diagnostic information for remote patient care.
This remote access is precious in rural or underserved areas, where access to specialized healthcare services may be limited. By leveraging DICOM viewers in telemedicine, healthcare providers can ensure patients receive the necessary care regardless of location.
DICOM medical viewers support virtual consultations by allowing healthcare providers to share and discuss medical images with patients in real time. These viewers enable physicians to visually explain their findings, diagnoses, and treatment recommendations, leading to better patient understanding and engagement.
As a result, patients can make more informed decisions about their healthcare and feel more confident in their treatment plans.
By providing remote access to medical images, DICOM viewers help to expand access to specialized care for patients in remote or underserved areas. Telemedicine allows patients to consult with specialists without needing time-consuming and costly travel.
Specialists can use DICOM viewers to review medical images, provide expert opinions, and collaborate with local healthcare providers to ensure patient care. This increased access to specialized care can lead to earlier diagnosis, more effective treatment, and improved health outcomes for patients in areas with limited healthcare resources.
As DICOM medical viewers facilitate the remote access and sharing of medical images, they also raise concerns about data privacy and security. Ensuring that patient information remains confidential and secure is paramount.
Healthcare organizations must implement strong security measures, such as encryption and access controls, to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or potential cyberattacks.
The successful implementation of DICOM medical viewers in teleradiology and telemedicine requires a robust technical infrastructure. Reliable, high-speed internet connections are essential for transmitting sizeable medical image files and enabling real-time consultations.
Additionally, healthcare providers must invest in compatible hardware and software to ensure seamless integration with their existing systems.
 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
Healthcare professionals must be comfortable using the technology to maximize the benefits of DICOM medical viewers. Ensuring that these viewers are user-friendly and accessible is crucial for their widespread adoption.
Training and ongoing support can help users become proficient in DICOM viewers and unlock their full potential in teleradiology and telemedicine.
As telemedicine and teleradiology continue to grow, healthcare organizations must navigate the complex legal and regulatory landscape surrounding these services.
Compliance with data protection regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States or the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, is essential.
Additionally, healthcare providers must address licensure, reimbursement, and medical malpractice issues to ensure the responsible and ethical delivery of remote healthcare services.
DICOM medical viewers play a pivotal role in advancing teleradiology and telemedicine. By enabling remote access to medical images, promoting collaboration among healthcare professionals, and enhancing the efficiency of patient care, these viewers have transformed the medical imaging landscape.
However, challenges like data privacy, technical infrastructure, and legal considerations must be addressed to realize their potential fully.
As medical imaging technology continues to evolve, integrating DICOM medical viewers in teleradiology and telemedicine will undoubtedly become increasingly important, shaping the future of healthcare delivery and improving patient outcomes worldwide.
|
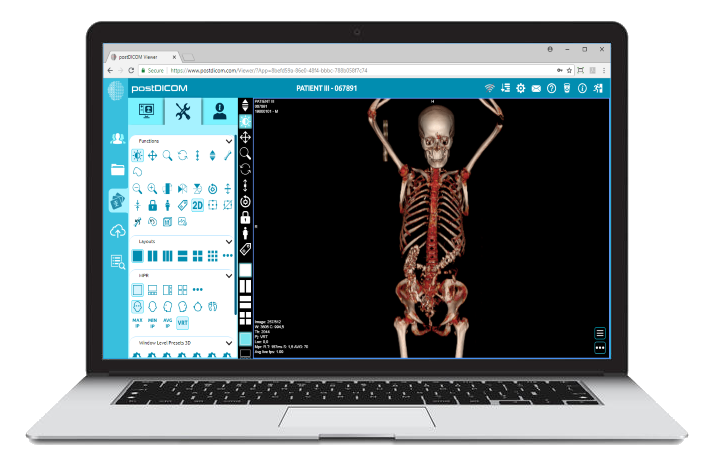
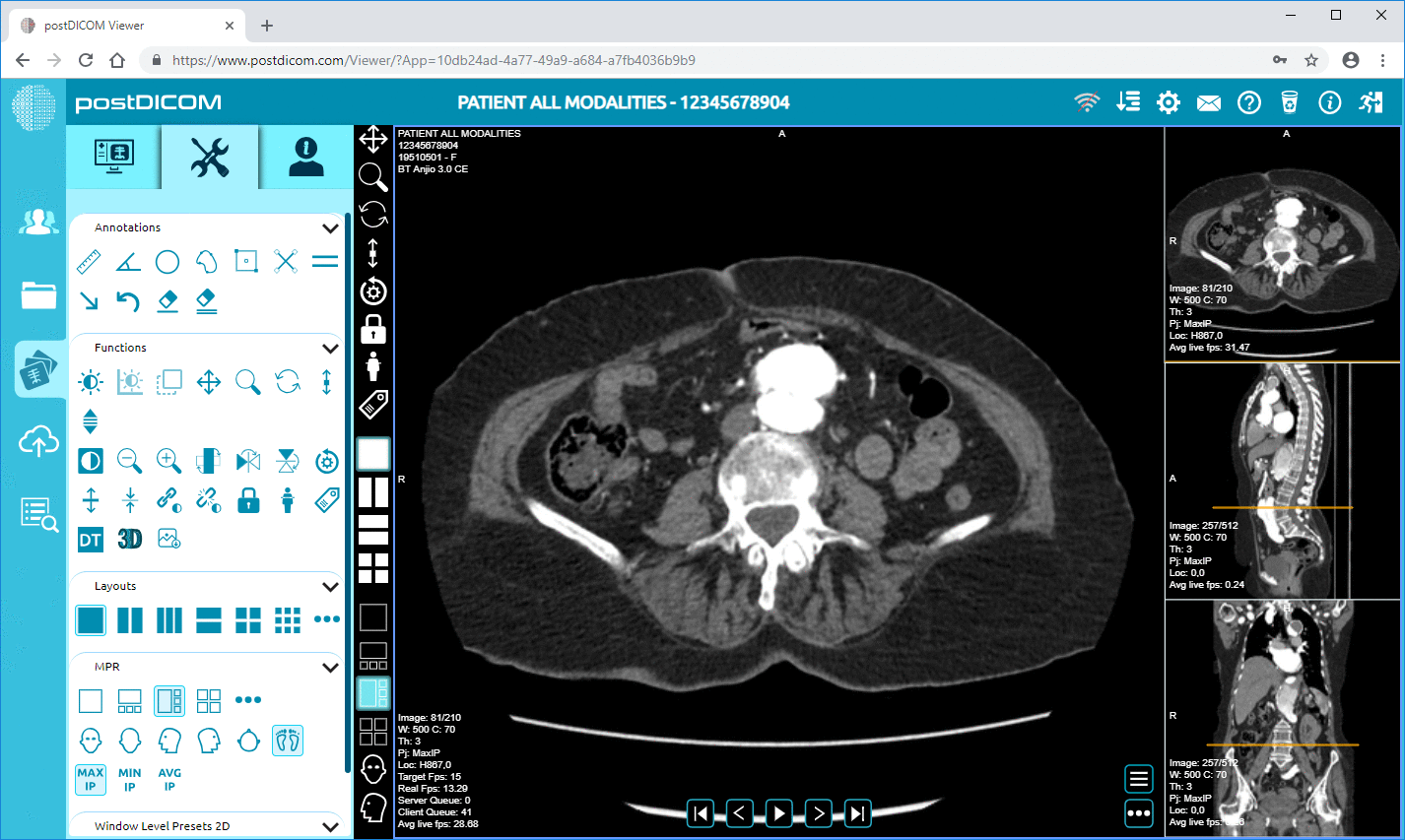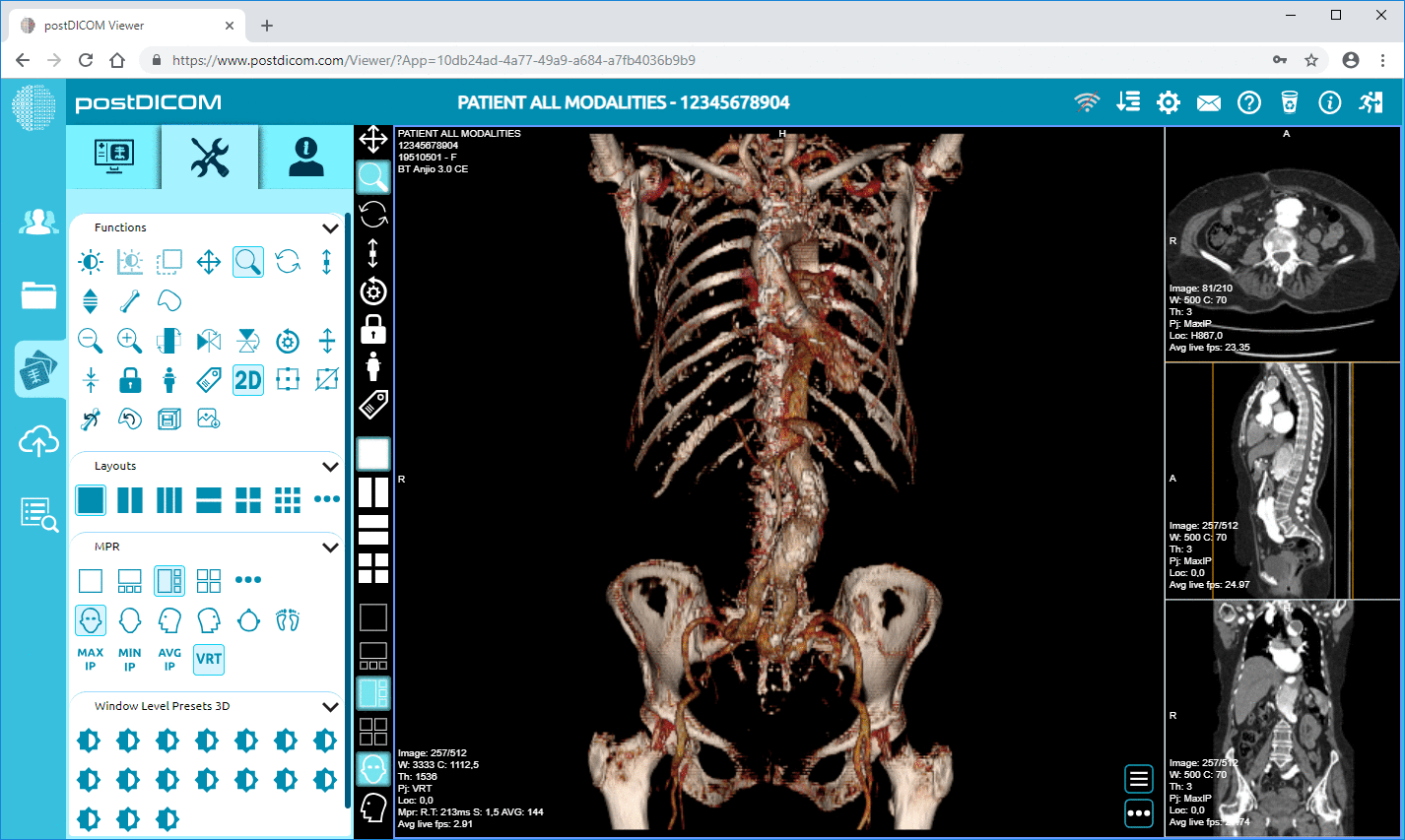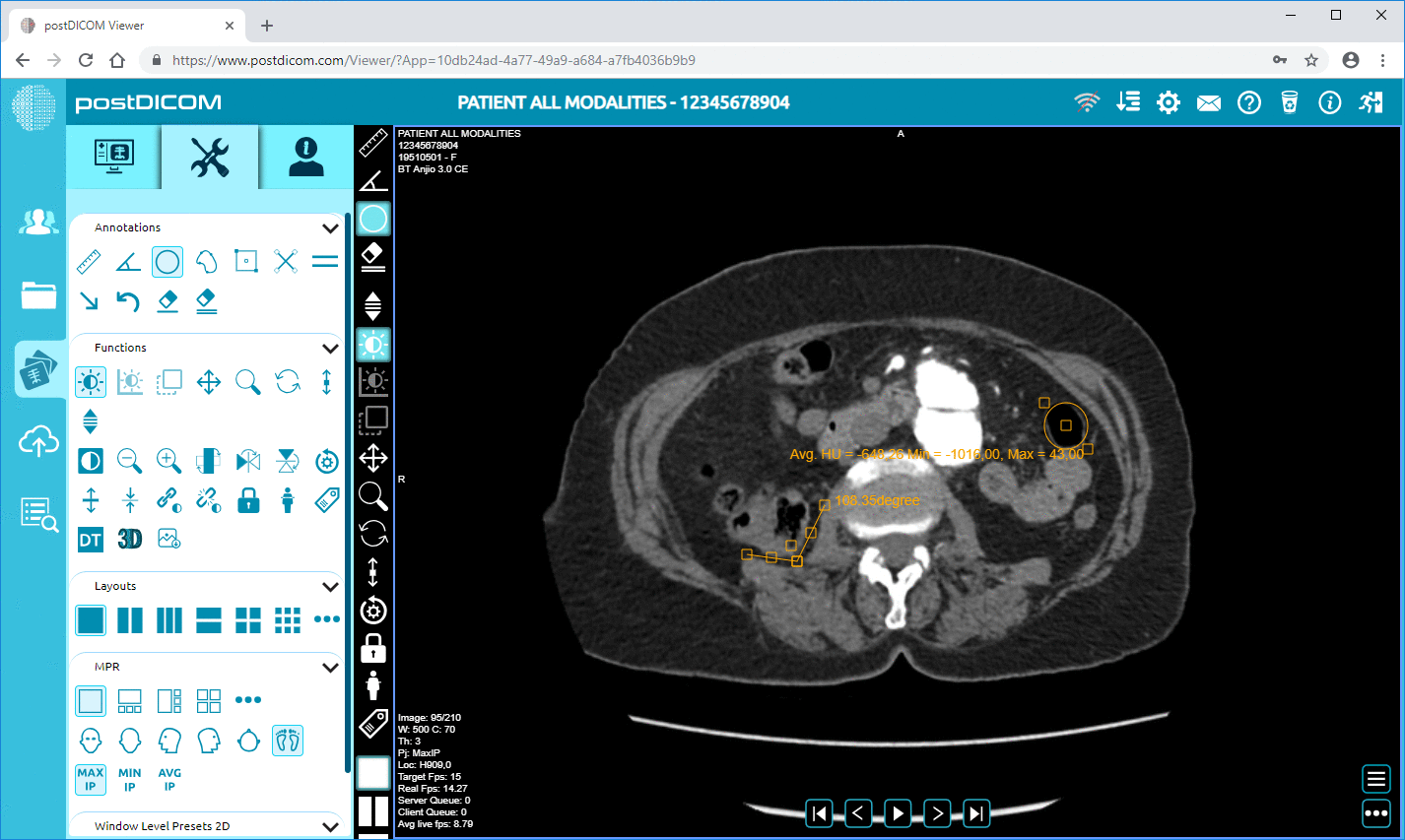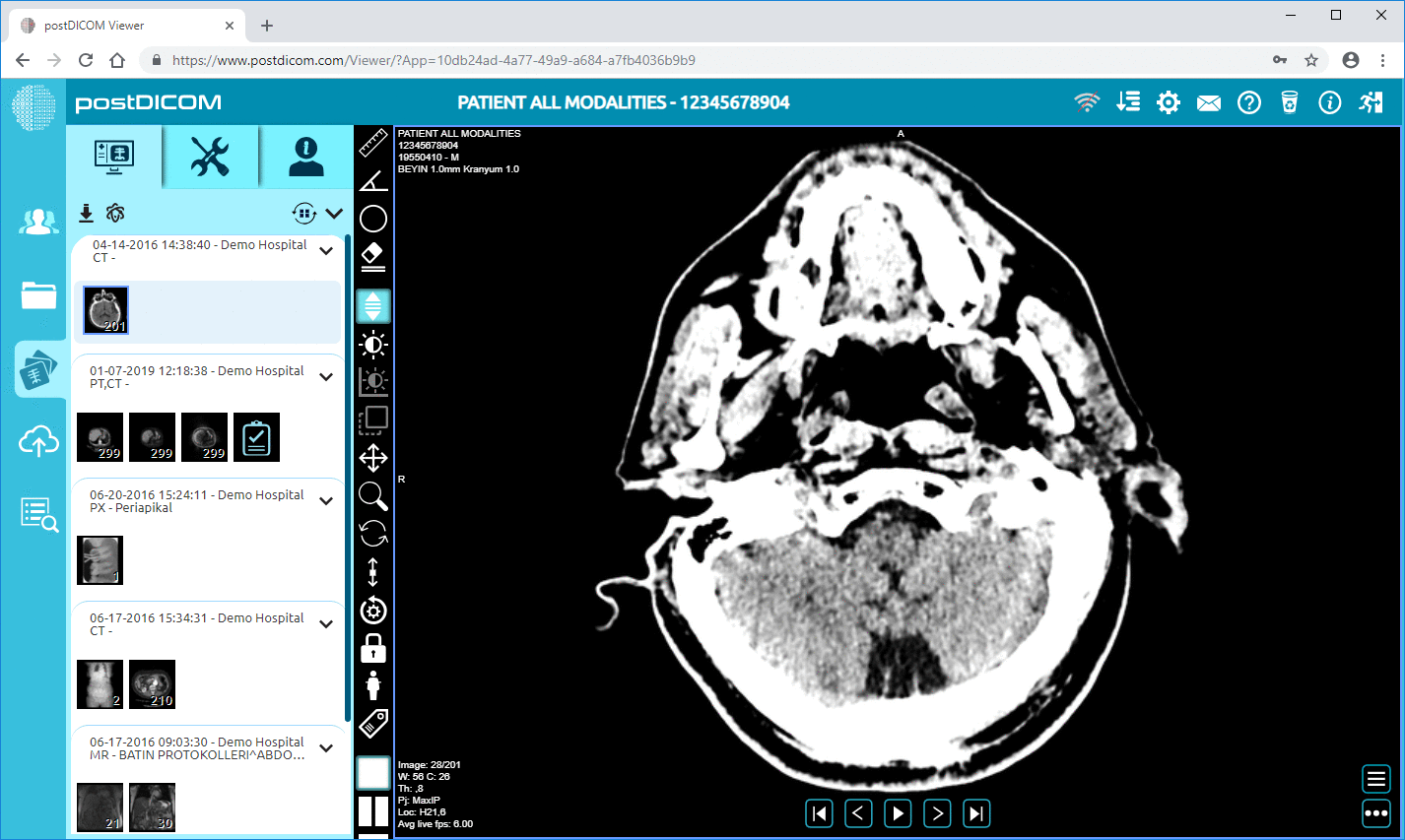
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |