In the world of modern healthcare, imaging technologies have become indispensable tools for diagnosing and treating a wide range of conditions. From cancer to neurological disorders, imaging provides essential insights into a patient’s health, helping doctors make accurate and timely decisions. As the demand for precision and comprehensive diagnostics grows, so does the need for integrated imaging solutions.
One such transformative solution is the Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS), which has significantly reshaped how medical images are stored, managed, and shared. PACS is not just a technological upgrade but a game-changer in supporting multimodal imaging—an approach combining multiple imaging techniques to offer a more complete picture of a patient’s condition.
In this blog, we’ll explore how PACS is helping streamline multimodal imaging, its healthcare benefits, and the exciting future of medical imaging.
Multimodal imaging uses multiple imaging techniques to comprehensively view a patient's health condition. It integrates various diagnostic imaging modalities, such as MRI, CT scans, PET scans, ultrasound, and X-rays, each providing different types of information. By combining these diverse imaging methods, healthcare professionals can gain more detailed insights into a patient’s condition than a single imaging technique.
Each imaging modality offers a unique perspective. For example:
• Mri(magnetic Resonance Imaging) Is Exceptional For Soft Tissue Imaging, Such As The Brain, Spinal Cord, And Muscles.
• Ct(computed Tomography) Provides Highly Detailed Cross-sectional Images Of Bones And Organs.
• Pet(positron Emission Tomography) Detects Metabolic Activity And Is Commonly Used In Oncology For Tumor Detection.
By integrating these different types of scans, clinicians can form a more accurate diagnosis and develop a targeted treatment plan. Multimodal imaging is particularly beneficial in fields like:
• Oncology: Combining PET and CT scans helps doctors assess tumor size, location, and potential spread.
• Neurology: Merging MRI and PET scans provides a more precise understanding of brain function and abnormalities.
• Cardiology: Combining echocardiograms with CT scans allows doctors to evaluate cardiovascular health comprehensively.
A Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) is a medical imaging technology that provides storage, retrieval, management, and sharing of medical images and associated data.
Traditionally, medical photos were stored in physical films, which was cumbersome and inefficient for modern diagnostic needs. PACS replaced these traditional film-based methods with digital solutions, allowing images to be stored electronically and accessed instantly.
The primary functions of PACS include:
• Storing Medical Images: PACS centralizes all imaging data, including those from X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, ultrasounds, and more.
• Retrieving Images: Healthcare professionals can access images from anywhere, at any time, through a digital interface.
• Managing Images: PACS ensures the proper storage, organization, and secure access to patient data.
• Facilitating Real-time Access And Sharing: PACS allows medical images to be shared between departments or even across healthcare institutions, improving collaboration between specialists.
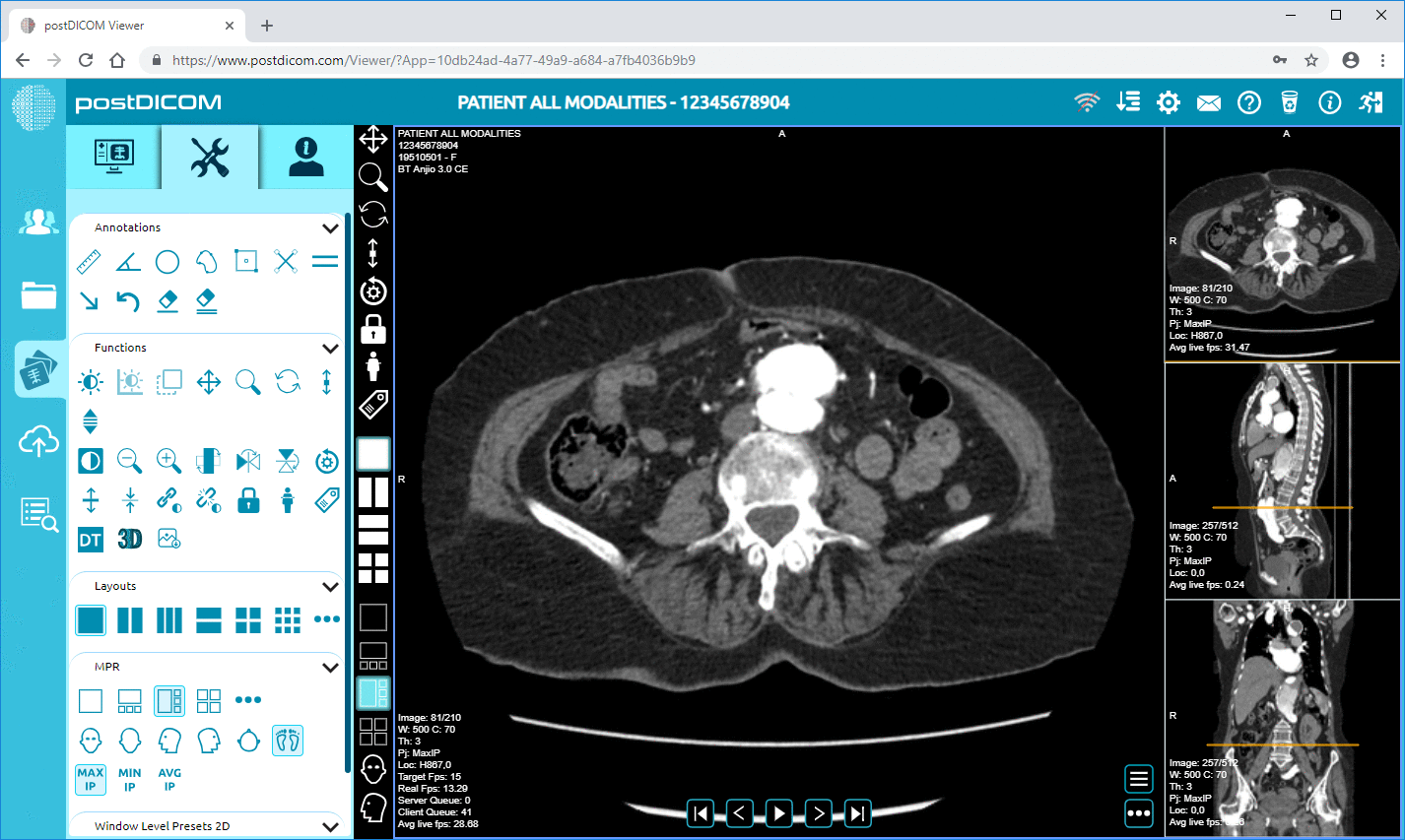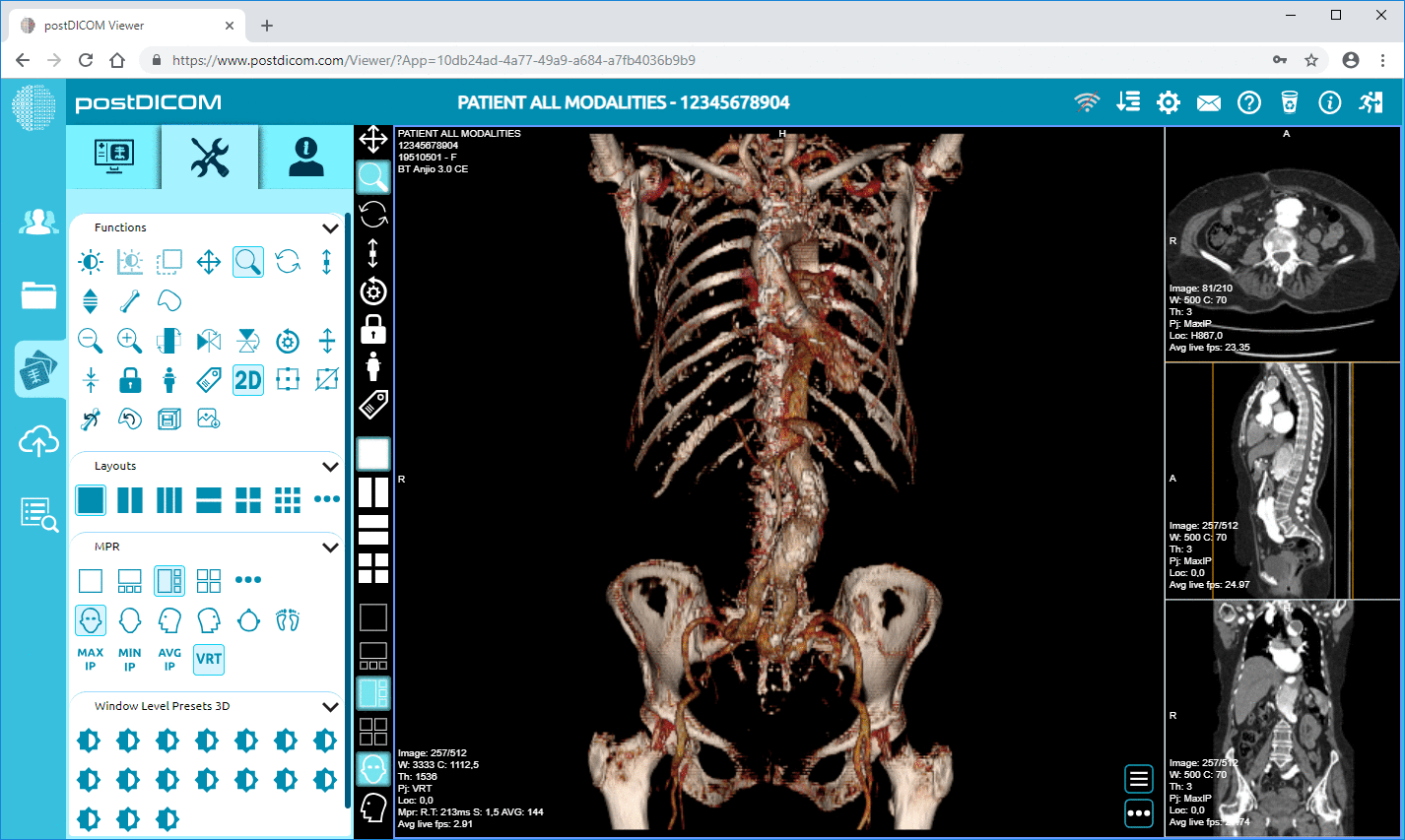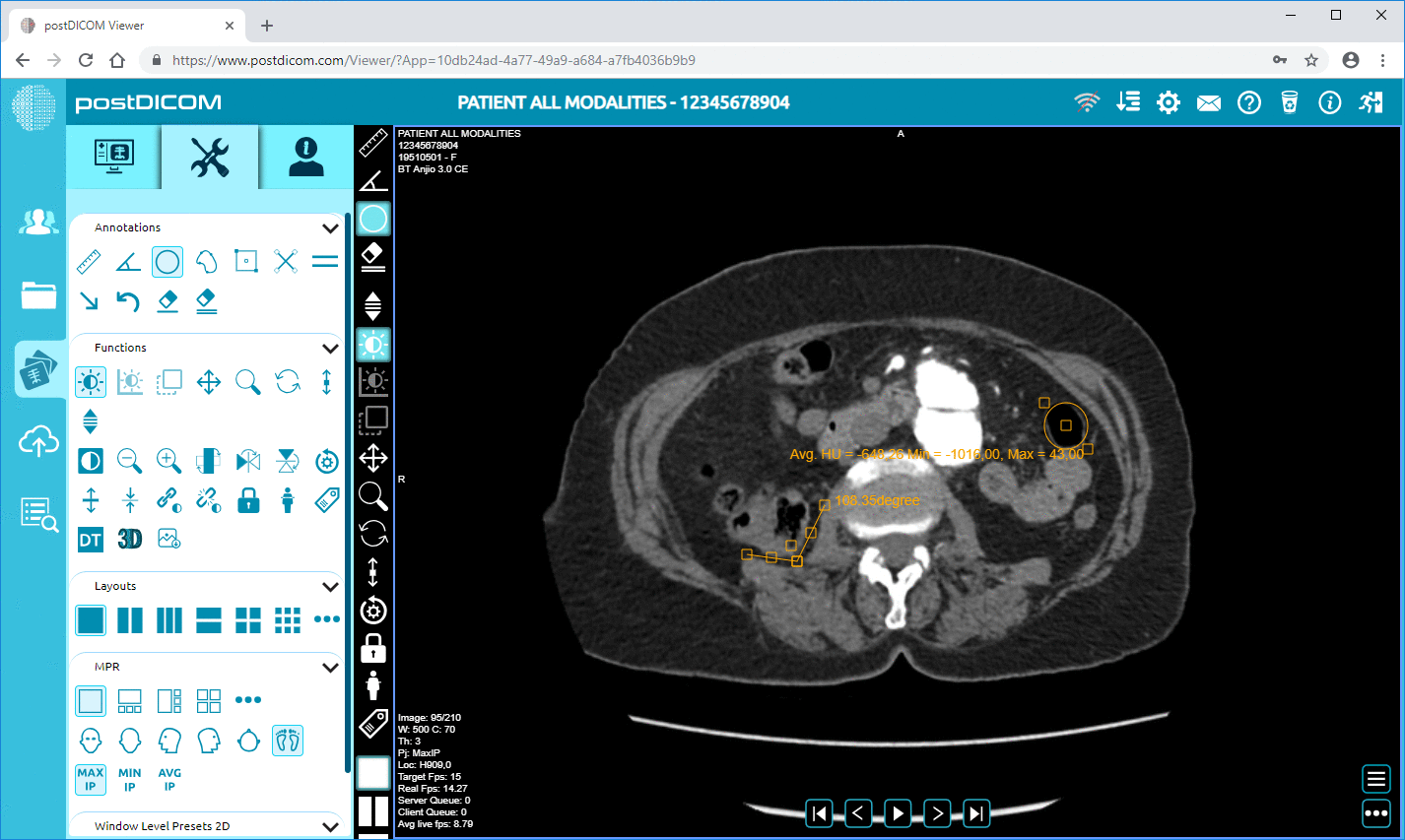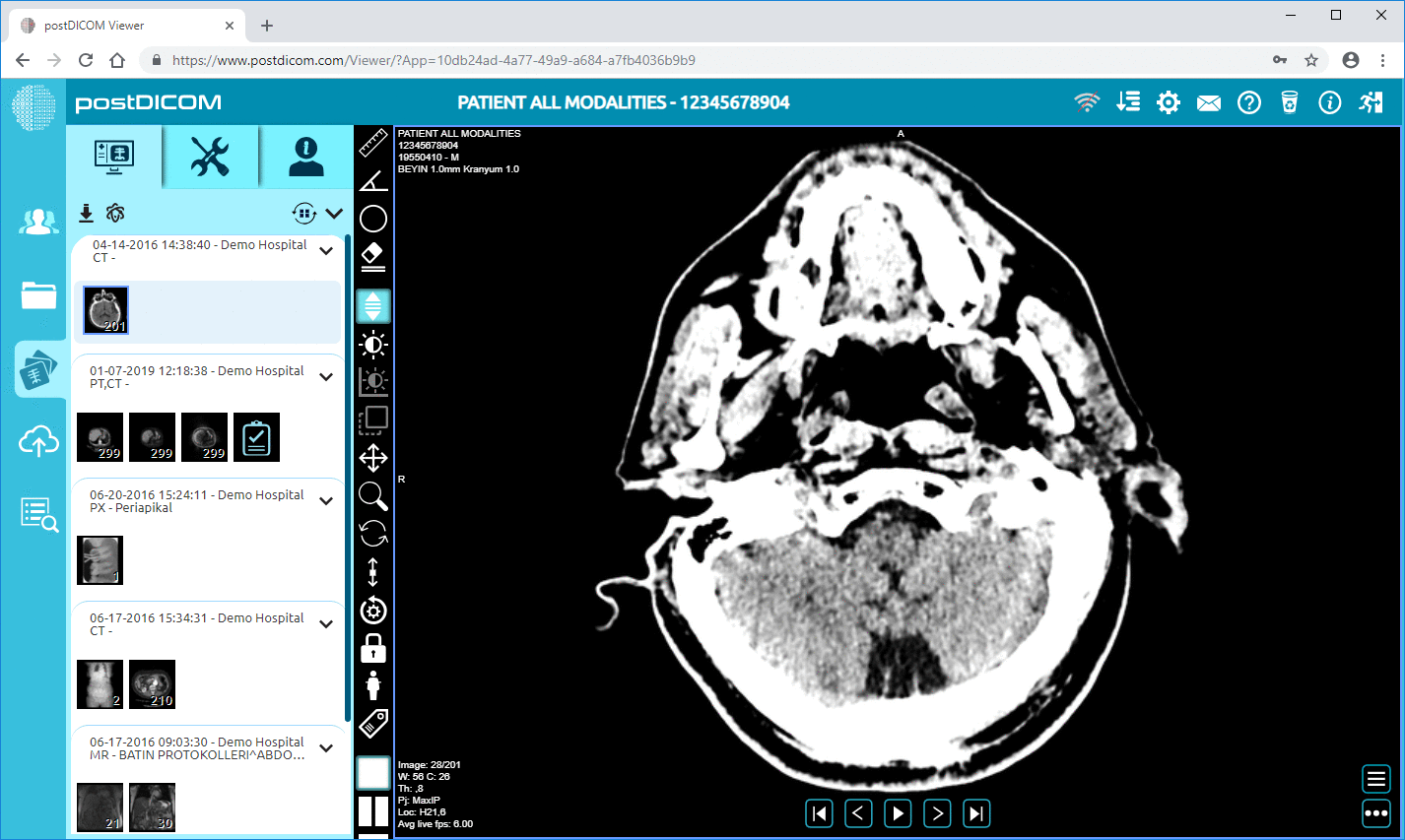
A multimodal image is created by combining different imaging techniques into a single, unified dataset. These images can be made by merging or fusing scans from modalities like CT, MRI, PET, and others. Specialized software aligns, registers, and combines these images, ensuring that all imaging techniques are accurately overlaid.
For example, consider a patient undergoing cancer treatment. A PET scan might show where the cancerous tissue is metabolically active, while an MRI could reveal the precise location and structure of the tumor. Combining these images into one multimodal image allows doctors to see both the tumor's biological activity and structural details, providing a more complete picture of the patient's condition.
The use of multimodal images is particularly beneficial in:
• Cancer Diagnosis: Overlaying PET and CT images can help clinicians detect tumors and evaluate their size, shape, and spread.
• Neurological Disorders: Combining CT and functional MRI images helps detect brain abnormalities, improving diagnostic accuracy.
• Cardiovascular Disease: Multimodal imaging helps doctors visualize the heart's function and structure, leading to better treatment planning.
The process of creating and using multimodal images involves several critical steps:
1. Acquisition Of Individual Scans: The first step involves taking images from different modalities, such as CT, MRI, or PET. These images provide unique insights into the patient’s condition.
2. Image Processing And Enhancement: Once the individual images are obtained, they are processed and enhanced to ensure clarity and accuracy.
3. Registration And Fusion: Specialized software aligns and fuses the images from different modalities to create a single multimodal image. This process is known as image registration.
4. Storage And Retrieval: After fusion, the multimodal images are stored in PACS, making them easily accessible for future reference.
5. Ai-driven Analysis: Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are increasingly important in automating the fusion and analysis of multimodal images, improving diagnostic accuracy and reducing human error.
PACS plays a crucial role in this process by enabling the seamless synchronization of multimodal images. With cloud-based PACS solutions, clinicians can access these images from any location, enhancing collaboration and improving diagnostic workflows.
| Imaging Modality | PACS Integration | Benefits with PACS | Challenges Without PACS |
| CT (Computed Tomography) | Seamlessly integrates with PACS for storage and sharing | Quick access to images, enhanced collaboration, and easy retrieval | Difficulty accessing images across departments, data fragmentation |
| MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) | PACS enables storage, retrieval, and sharing of high-resolution MRI scans | Real-time sharing among specialists for faster diagnosis | Delays in accessing and sharing images without PACS |
| PET (Positron Emission Tomography) | PACS allows fusion of PET and other imaging modalities (e.g., CT, MRI) | Improved diagnostic accuracy through combined images | Separate systems for different modalities, leading to inefficiency |
| Ultrasound | Integration with PACS for real-time image access and sharing | Streamlined workflows, access to archived images for comparison | Limited data synchronization, fragmented workflows |
| Echocardiography | PACS stores and integrates ultrasound and echocardiography data | Easy comparison with other imaging types (CT, MRI) for cardiovascular assessments | Lack of integration, leading to inefficiency in diagnosis |
Without PACS, managing multimodal images can be a daunting task. Some of the key challenges include:
• Data Fragmentation: Different imaging modalities often require separate storage systems, making it difficult to view all patient images in one place.
• Compatibility Issues: Proprietary image formats used by different imaging devices can create barriers to sharing data between systems, leading to delays in diagnosis.
• Storage Limitations: Large image datasets, particularly those generated from high-resolution scans, require substantial storage capacity. Traditional storage solutions may not be able to handle the volume and size of modern medical images.
• Delayed Diagnostics: Without a unified system like PACS, accessing and sharing images can take time, potentially delaying diagnosis and treatment.
• Security And Compliance Concerns: Healthcare organizations must ensure that patient data is stored and shared in compliance with HIPAA regulations. Without a secure PACS solution, protecting patient confidentiality becomes a challenge.
 - Presented by PostDICOM.jpg)
PACS is revolutionizing multimodal imaging in several significant ways:
1. Centralized Image Management: PACS centralizes all medical images, including those from various imaging modalities, in one place. Physicians can access comprehensive imaging records quickly, improving workflow efficiency.
2. Seamless Interoperability: Modern PACS solutions integrate with various imaging modalities and systems likeDICOMandHL7, allowing healthcare providers to share and access images without fearing vendor lock-in. This interoperability facilitates collaboration across departments and institutions.
3. Ai-driven Image Fusion And Analysis: AI-powered PACS solutions automate the fusion of multimodal images, improving the accuracy and efficiency of diagnoses. Deep learning algorithms can analyze patterns across various imaging techniques, helping to detect abnormalities that might go unnoticed by human eyes.
4. Enhanced Accessibility With Cloud Pacs: Cloud-based PACS, such as PostDICOM, ensure instant access to multimodal images from anywhere. This is particularly valuable for remote consultations and second opinions, as specialists can access patient data without being on-site.
5. Cost Efficiency And Scalability: Traditional PACS systems often require significant upfront investment in hardware and infrastructure. Cloud PACS offers a scalable solution that eliminates costly storage upgrades, making it a more cost-effective option for healthcare organizations.
The future of multimodal imaging is bright, with several exciting advancements on the horizon:
• Ai And Machine Learning: AI-powered PACS solutions will continue to enhance diagnostic accuracy by automating the analysis of multimodal images.
• 5g Technology: With the rollout of 5G networks, real-time sharing of large medical images will become even faster, facilitating quicker diagnoses and remote consultations.
• Blockchain: Integrating blockchain technology into PACS will improve data security and patient confidentiality, ensuring that medical images and information remain safe and tamper-proof.
• Ar And Vr: Augmented and Virtual Reality technologies will offer new ways for healthcare professionals to interact with multimodal images, improving surgical planning, medical education, and patient care.
PACS is undeniably transforming the landscape of multimodal imaging, making it easier for healthcare providers to access, manage, and share medical images. With its ability to centralize image data, enhance collaboration, and integrate AI-powered analysis, PACS plays a crucial role in improving diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes.
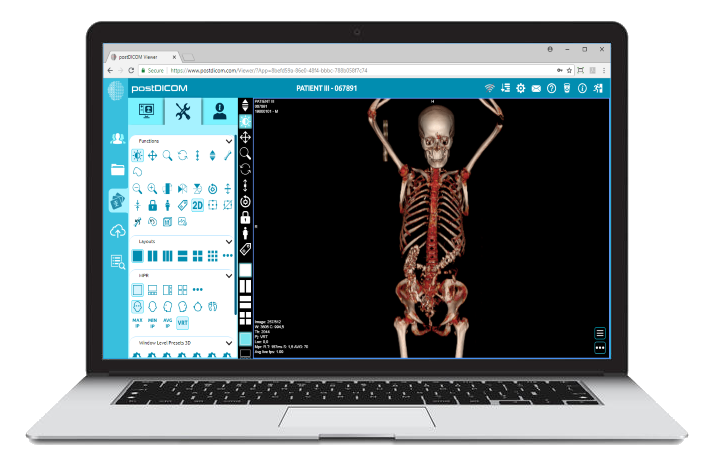
Cloud-based PACS solutions like PostDICOM offer healthcare providers a seamless, scalable, and cost-effective way to manage multimodal images, providing a comprehensive view of patient health. As technology evolves, PACS will remain at the forefront of medical imaging, driving diagnostics and treatment planning advancements.
Are you ready to experience the future of medical imaging? Sign up for a free trial of PostDICOM today and explore how our advanced PACS solution can help streamline your healthcare workflows and improve patient care.
|
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |