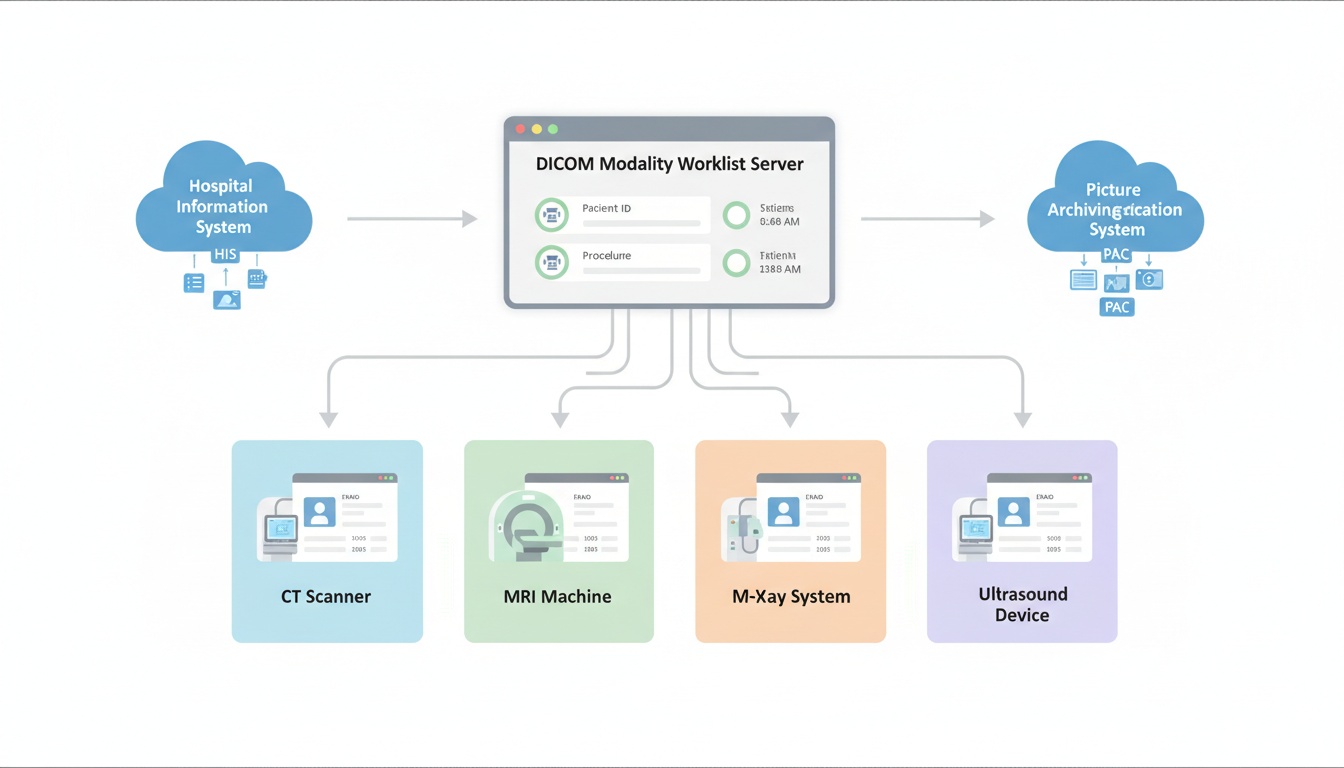
The DICOM Modality Worklist (DMWL) is a critical component of the Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) standard, playing a vital role in modern medical imaging.
By automating data transfer and streamlining workflows, it enhances the efficiency and accuracy of imaging departments.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of DICOM worklists, exploring their definition, purpose, structure, benefits, challenges, and relevant standards.
A DICOM Modality Worklist in medical imaging is an electronic list that schedules imaging procedures and provides patient information on imaging modalities such as MRI, CT, X-ray, and ultrasound systems.
This list includes crucial details like patient demographics, the procedure ordered, and relevant clinical information. The worklist is dynamically updated and shared across the network, ensuring that imaging devices and operators can access the most current and relevant information.
DICOM worklists streamline imaging workflows by automating the flow of patient and study data between medical imaging systems and devices.
They integrate with healthcare systems like Radiology Information Systems (RIS) and Hospital Information Systems (HIS) to ensure seamless communication of imaging orders and patient details.
DICOM worklists significantly enhance radiology workflow efficiency. By automating data transfer and eliminating manual data entry, they reduce the risk of human error and free up valuable time for radiology staff, allowing them to focus on patient care and other critical tasks.
The key functions of a DICOM worklist include:
• Eliminating Manual Data Entry: The worklist pulls patient demographics, study details, and imaging orders from RIS and HIS, ensuring imaging devices have accurate and consistent data for every procedure. This automation saves time and reduces the risk of errors associated with manual data entry.
• Improving Data Accuracy: Leveraging a centralized worklist ensures accurate and up-to-date patient information, crucial in medical imaging to prevent incorrect imaging, misdiagnoses, or delayed treatments. Precise patient data is paramount for effective diagnosis and treatment planning.
• Streamlining Workflow: It automates the transfer of patient and procedure information from RIS or HIS to the imaging modality, reducing the chances of human error and freeing up valuable time for radiology staff. This streamlined workflow contributes to increased efficiency and productivity in the imaging department.
• Improving The Efficiency Of Medical Imaging Procedures: DICOM worklists help enhance efficiency by ensuring that the correct patient information is readily available to the imaging technologist. This reduces the time spent searching for and verifying patient data, allowing quicker and smoother procedures.
• Facilitating Interoperability: It enables seamless communication between different departments and systems within a healthcare facility, ensuring better coordination and continuity of care. Interoperability is essential for efficient information exchange and collaboration among healthcare providers.
• Accessing Prior Studies: DICOM worklists can pull prior studies from various sources, streamlining the process for clinicians and radiologists. Access to previous studies provides valuable context for current imaging procedures, enabling more informed decision-making and potentially reducing the need for repeat examinations.
• Ensuring Correct Patient Identification: The DICOM modality worklist is crucial for correctly associating the correct patient to the images and communicating that information to other devices or systems. This accurate patient identification is essential for preventing medical errors and ensuring that the right patient receives the appropriate care.
The DICOM standard defines the structure of a DICOM worklist and specifies its format and content. Each worklist item represents a single task and contains attributes from different objects related to that task.
In a filmless radiology department, three core computer systems—the Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS), the Hospital or Radiology Information System (HIS/RIS), and the acquisition modality—ideally have bidirectional communication. The DICOM worklist plays a crucial role in this communication network.
Modalities query the worklist to find the next patient and retrieve the partial DICOM file. This partial file contains patient and study data but no images. The modality then performs the study, creating a series of images for each task required. Radiologists then push this information to the PACS for storage and retrieval.
The essential components of a DICOM worklist are categorized and presented in the following table:
| Component Category | Component |
| Patient Demographics | Patient ID |
| Patient Name | |
| Patient Birth Date | |
| Patient Gender | |
| Study Information | Study ID |
| Accession Number | |
| Referring Physician | |
| Study Description | |
| Scheduled Procedure Step | Start Date and Time |
| Modality | |
| Requested Procedure ID | |
| Requested Procedure Description | |
| Scheduled Station AE Title | |
| Performing Physician | |
| Location | |
| Pre-Medication | |
| Special Needs |
DICOM worklists are used in various medical imaging modalities, ensuring efficient and accurate imaging procedures across different departments.
In X-ray imaging, the worklist provides the X-ray technician with patient information and the specific X-ray procedure, ensuring the correct procedure is performed on the correct patient. This eliminates the need for manual data entry, reducing the risk of errors and improving efficiency.
The worklist automatically provides CT scans with patient demographics, study details, and imaging orders, eliminating manual data entry and reducing errors. This automation streamlines the workflow and ensures that the CT scanner has the necessary information to perform the scan accurately.
In MRI, the worklist ensures that the MRI scanner has the correct patient and study information, which is crucial for accurate imaging and diagnosis. This helps prevent misidentification and ensures that the MRI examination is tailored to the specific patient and clinical question.
 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
DICOM worklists offer numerous benefits in medical imaging but also present some challenges that must be addressed.
• Reduced Errors And Improved Efficiency: DICOM worklists minimize patient information errors and enhance the accuracy of the accuracy of imaging procedures by automating data transfer and eliminating manual entry. This automation streamlines workflows, saving time and resources by automating tasks and reducing manual effort.
• Standardized Data Exchange: They standardize patient information exchange between devices, improving interoperability and communication between different systems. Standardized data exchange facilitates seamless information flow and collaboration among healthcare providers.
• Enhanced Patient Care And Improved Workflow, Diagnosis, And Patient Care: Worklists improve patient care and outcomes by ensuring accurate and efficient imaging procedures. DICOM, including its worklist functionality, has significantly improved workflow, diagnosis, and patient care in medical imaging. These improvements improve healthcare outcomes by enabling faster and more accurate diagnoses, leading to more effective treatment plans.
• Compatibility Issues: Variations in DICOM implementations by different vendors can lead to compatibility issues and hinder seamless communication between systems. Ensuring compatibility among vendor systems is crucial for seamless data exchange and interoperability.
• Data Inconsistencies: Inconsistencies in data formats and metadata tagging can create challenges in data exchange, potentially leading to mismatches or data duplication. Standardized data formats and metadata tagging are essential for accurate and efficient data exchange.
• Security Concerns: Secure DICOM implementations may require additional encryption and authentication processes, which can introduce delays or technical issues in image transmission. Balancing security with efficient data transfer is crucial in medical imaging.
• Performance Impact: Secure DICOM protocols can introduce latency and increase processing times, which can be a concern in clinical environments requiring rapid image access. Optimizing secure DICOM protocols to minimize performance impact is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment.
• Body Part Ambiguity: While DICOM's naming structure for body parts is standardized, it can sometimes be overly specific or need to be more detailed, leading to ambiguity. Unambiguous anatomical terminology is crucial for accurate image interpretation and communication.
• Color Standardization: Specialties that rely on medical photography, such as dermatology and pathology, can find color standardization challenging due to variations in lighting, shadowing, and camera settings. Consistent and reproducible color representation is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning in these specialties.
DICOM worklists are subject to the DICOM standard, which defines the technical specifications for medical image communication and management. The standard ensures interoperability between different medical imaging devices and systems and guarantees seamless data exchange and communication in medical imaging.
Regulations like HIPAA in the U.S. mandate safeguarding patient information, including data handled by DICOM worklists. These regulations ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of patient data. Compliance with these regulations is essential for protecting patient privacy and maintaining data security.
DICOM worklists play a vital role in modern medical imaging by streamlining workflows, improving data accuracy, and enhancing patient care. While compatibility, data consistency, and security exist, the benefits of using DICOM worklists outweigh the challenges. By adhering to the DICOM standard and relevant regulations, healthcare facilities can leverage the full potential of DICOM worklists to optimize their imaging operations and improve patient outcomes.
DICOM worklists will become even more integrated with other healthcare systems and technologies as medical imaging technology evolves. The increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in medical imaging workflows presents opportunities for further automation and optimization of imaging procedures.
DICOM worklists can facilitate the integration of AI and machine learning algorithms into medical imaging workflows by providing standardized and structured patient and study data.
This integration has the potential to improve further the efficiency, accuracy, and effectiveness of medical imaging, ultimately leading to better patient care and outcomes.
|
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |